Revealed October 20, 2025 01:37PM
Again in 2019, scientists proposed a new theory of endurance. For efforts lasting greater than a few day, they advised, the last word restrict is dictated by how a lot meals you’re in a position to digest. Your coronary heart and thoughts and muscle mass can adapt to do superb issues, however all of them want gasoline. Probably the most energy you may digest appears to be about 2.5 instances your resting metabolism—in order that’s what limits how a lot bodily exercise you are able to do day after day over weeks, months, or years.
This concept of a “metabolic ceiling” sparked a lot of dialogue, however it additionally left some open questions. Does it actually apply to top-level endurance athletes—like, say, Kilian Jornet, who simply completed climbing 72 1,400-foot summits and biking 2,500 miles in simply 31 days whereas quaffing olive oil for energy? A newly revealed research in Current Biology units out to reply a few of these questions, measuring calorie information from 14 world-class ultrarunners and triathletes and analyzing the coaching logs of notable athletes like Jornet. Right here’s what they discovered.
What They Did
The research was led by Andrew Better of the Massachusetts Faculty of Liberal Arts and Herman Pontzer of Duke College, the latter of whom was one of many key authors of the unique 2019 paper. The important thing information within the paper comes from 14 ultra-endurance athletes who drank particular isotope-labeled water that enabled the scientists to calculate precisely what number of energy they have been burning at completely different instances. They collected this information throughout occasions like a six-day ultramarathon, a 24-hour document try, and Joe McConaughy’s 13-day FKT on the Arizona Path. Additionally they collected calorie information throughout a number of coaching weeks, for causes we’ll get into under.
The calorie information from races blew by means of the theorical restrict of two.5 instances resting metabolism. That’s as a result of you may afford to enter calorie debt for brief intervals of time, that means that you just’re burning saved fats (and generally muscle) and losing a few pounds. “Joe misplaced tons of weight working the Arizona Path,” Finest informed me. However that may’t proceed indefinitely. Should you’re burning 9,000 energy a day (as Jornet estimates he was throughout his most up-to-date problem) however solely consuming 7,000 energy a day, you would possibly be capable of preserve doing that for a month or two, however you’ll ultimately hit a wall.
That’s why Finest additionally measured energy throughout coaching weeks. By taking at the least two measurements for every runner, one throughout a contest or laborious coaching week and the opposite throughout a comparatively simple coaching week, he created a customized formulation for every runner to estimate what number of energy they burn as a operate of how a lot they’re working. Then he utilized this formulation to a yr’s price of coaching information to see what number of energy they may burn over a 12-month interval fairly than simply throughout every week or two of competitors. That’s the place the two.5 resting metabolism restrict reveals up once more.
Right here’s a graph exhibiting “metabolic scope” (which is what number of energy per day you’re burning expressed as a a number of of resting metabolism) for various durations:
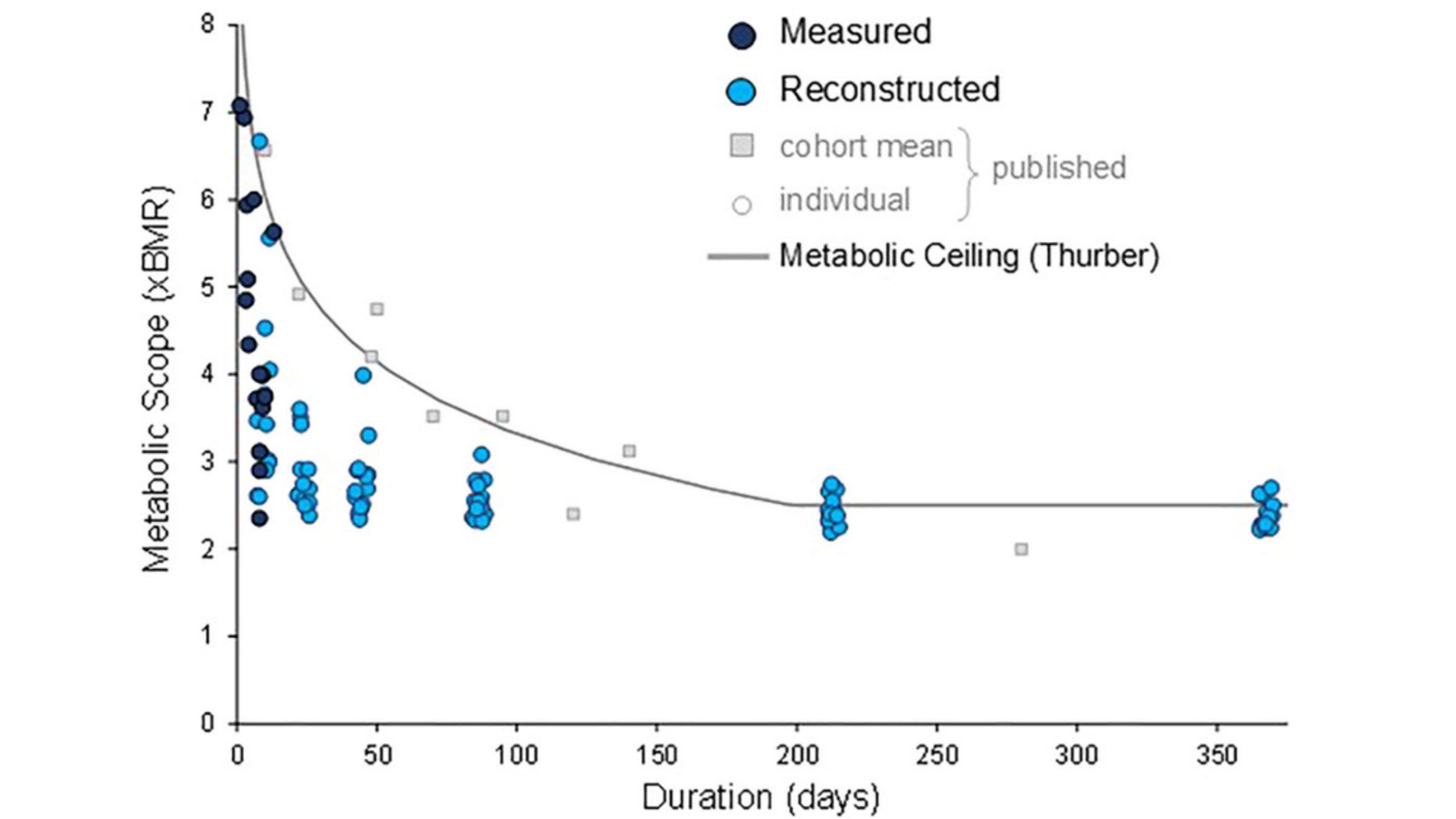
The darkish blue circles on the left aspect of the graph present the direct measurements of calorie burn throughout coaching and racing. There are values as excessive as seven instances resting metabolism, which corresponds to a one-day document try on a 90-mile path.
The sunshine blue circles are calculated from the athletes’ coaching logs based mostly on coaching intervals of assorted lengths. For instance, on the six-week mark (42 days), you may see a spread of sunshine blue circles between about 2.5 and 4. The circle at 4 corresponds to a runner who ran an astounding 1,989 miles over a six-week interval, which is 332 miles per week. However that was throughout a 46-day FKT try on the Appalachian Path, so clearly not a stage the topic might maintain for a complete yr.
As you prolong to longer durations like 30 or 52 weeks, you may see that the sunshine blue circles all cluster round 2.5. Some are somewhat larger, others somewhat decrease, however none of those elite extremely athletes are sustaining values which can be considerably larger than the proposed restrict.
What about true super-elites like Kilian Jornet and triathlon star Kristian Blummenfelt? Based mostly on their publicly accessible coaching information, together with the coaching hours-to-calories formulation that the brand new research generated, Finest estimates that Blummenfelt averages about 2.8 to 2.9 instances his resting metabolism over the course of a complete yr, whereas Jornet hits 2.75. So the most effective of the most effective might edge barely above the standard restrict of two.5, however not by a lot.
What It Means
There are two fascinating options within the graph I included above. The primary and most essential is the flat line on the suitable aspect of the graph, which corresponds to the proposed asymptote of two.5 based mostly on the boundaries of digestion. The brand new outcomes bolster my confidence that this actually is a constant phenomenon. If Jornet isn’t breaking it (by a lot), I don’t know who’s. So I used to be shocked, once I checked in with Herman Pontzer, to seek out that he’s much less assured than he was in 2019 that that is an ironclad rule.
Certainly one of his causes is that extra information has emerged from elite cyclists at Grand Excursions the place they appear to be burning monumental numbers of energy with out losing a few pounds—which suggests that they’re absorbing a comparable variety of energy. A study of seven cyclists within the Giro d’Italia, for instance, discovered that they burned greater than 4 instances their resting metabolism over the course of 24 days with out losing a few pounds. It could be that sports activities scientists’ quest to supply ever-more digestible carbohydrates is enabling cyclists to push again the boundaries of digestibility.
The opposite fascinating characteristic within the graph is the form of the curve on the left. You see the same curve once you plot your pace in shorter distance (i.e. a couple of hours or much less) races towards the time elapsed, as I did for my very own monitor instances here. In that state of affairs, the asymptote corresponds to a amount known as important pace, which represents your long-term sustainable tempo. The form of the curve is dictated by one other parameter generally known as anaerobic capability, which you’ll be able to consider (very loosely) as the quantity of power you’re in a position to “borrow” when working quicker than important pace earlier than you hit a wall. Milers and different middle-distance runners are likely to have a really excessive anaerobic capability.
One thing has to dictate the form of Pontzer’s multi-day power curve, and at this level he’s unsure what that one thing is. Intuitively, you may consider it as analogous to anaerobic capability: you may “borrow” numerous energy for a brief time period, placing you means above the two.5 line; or you may borrow a lesser quantity over an prolonged time period. If you wish to preserve going for, say, six months, you may’t actually borrow something: energy out needs to be balanced by energy in.
However what determines the form of that curve? Should you’re carrying numerous physique fats, does that allow you to borrow extra for longer? Or, extra possible, in case you’ve educated your metabolism to burn fats extra quickly, does that elevate the curve? Does the exact form of the curve depend upon the combo of fats and carbohydrate that you just burn at completely different train intensities? Or are there different non-metabolic elements that come into play, like muscle restoration or psychological fatigue? The physiology of multi-day endurance challenges remains to be a comparatively younger scientific area—which implies there needs to be a lot of extra insights, and plenty extra enjoyable, nonetheless to return.
For extra Sweat Science, be a part of me on Threads and Facebook, join the email newsletter, and take a look at my new e book The Explorer’s Gene: Why We Seek Big Challenges, New Flavors, and the Blank Spots on the Map.








